"What intrigues us as a problem, and what will satisfy us as a solution, will depend upon the line we draw between what is already clear and what needs to be clarified," Nelson Goodman.
State Space Models
Saturday, December 21, 2024
World-System (1970-2060) US Debt Crisis
Thursday, December 19, 2024
World-System (1980-2060) Five Futures for Russia (one surprised me)
Now that the Syrian Regime has collapsed (here), questions about what the collapse will mean for Russia are begin discussed (here). Russia did not intervene when rebels overran the Syrian capital and the question is "why" given that Syria fought not be become a Russian puppet state (a topic I will cover in a future post). In this post, I will concentrate on some possible future geopolitical alignments for Russia, one of which is to go it alone (BAU). One of the interesting and controversial models is to link to the EU, which would be by far the best choice for Russia, the least likely to happen in the medium term future and certainly the least discussed openly right now.
- BAU The Business As Usual model is unstable and cyclical (you can run the model yourself here). BAU is a fairly good model but not the best model (91.26 < AIC = 130.2 < 163.5). Unfortunately, the BAU model encourages military expansion because currently Russia needs Ukraine to prevent a Malthusian Population Crisis (to be covered in a future post).
- RW The Random Walk model would be best interpreted as a descent into Chaos, today being like tomorrow except for random shocks. The RW is actually not a bad competitor model for Russia (110 < AIC = 128.9 < 147.3) and may be quite likely if Russia looses the War in Ukraine.
- W Rather than isolating itself (BAU model), the World Linkage model assumes that Russia becomes an Open Society with Political and Economic links to all countries in the World-System (right now, Russia is a Semi-peripheral authoritarian country trying to become a Core country through military force). The W-Linkage model is not a very good competitor (126.4 < AIC = 155.6 < 190.1) and retains the unstable cyclical nature of the Russian System.
- US Linking to the US has never been seriously pursued in Russia, although the Glasnost period in the 1980s is about as close as the two countries came (67.98 < AIC = 114.3 < 150.7)--maybe because it would lead to cyclical collapse for Russia.
- EU Russia joining the European Union (EU) is, to me (somewhat surprisingly), the best option (of the models considered here) for Russia (58.25 < AIC = 102.2 < 144). It would allow Russia to continue growing exponentially and benefit from trade with the EU (particularly oil, natural gas and agricultural trade with Ukraine). Maybe this dream scenario will happen at some time in the distant future, but I am not holding my breath.
Notes
LCI is the lower confidence interval and UCI is the upper confidence interval. In probability, the system can clearly be stabilized.
The Axis of Evil
Tuesday, December 17, 2024
Has Germany Become a Steady State Economy?
Notes
Monday, December 9, 2024
World-System (1970-2050) Five Futures for Syria
- BAU The Business-as-Usual model is probably the best description of the Assad Regime. It was a unstable regime maintained by force. One fear about the collapse of the regime is that the future will be chaotic. Using the Akaike Information Criterion (AIC), the BAU model is one of the best models (-54.37 < AIC = -10.37 < 23.99) describing the SY20 system (see Notes below, the smaller the AIC, the better).
- US Diplomatic relations between Syria and the United States are currently "nonexistent". Syria was put on the State Sponsors of Terrorism list in 1979 and is the only country that has remained continuously on the list. From the period of the "War on Terror", the U.S. government has imposed a series of economic sanctions on Syria. After the government crackdown during the 2011 Syrian revolution; the US (alongside the European Union and Arab League) withdrew diplomatic recognition. The US has provided political, military and logistic support to the Syrian opposition. The new Syrian government might seek stronger linkages with the US, but the projections above are not very promising and somewhat unlikely (
107.6 < AIC = 161.3 < 203.3).
- RU Diplomatic relations between Russia and Syria have had, up to now, a long, friendly and stable history. Unfortunately for Bashar al-Assad (the current and now deposed president), Russia failed to defend the regime even though it had been providing military support up to the final coup. From the graphic above, the projection for Russia's support of Syria is cyclical and not much better than a Random Walk. The RU Puppet model, which Syria long resisted, would not be the best model for the future (97.65 < AIC = 162 < 219.9). Russia has it's own set of problems (not dissimilar to Syria) which I will cover in a future post.
- RW The Random Walk model essentially makes no predictions about the future except that tomorrow will be like today with the addition of random error. Notice that it is not much different from either the US, RU or World models when taken as input. For the RW model (55.99 < AIC = 95.64 < 125.5).
- W Maybe somewhat surprisingly, linking Syria with the World System would not produce a result much better than a random walk (119.4 < AIC = 177.1 < 217.6). However, in World-Systems Theory, Syria is a Peripheral Country with weak institutions and a small share of World wealth.
- MEA The worst possible future for Syria is linkage with the MiddleEast-Africa. Projections indicate a severe collapse for the system (97.65 < AIC = 162 < 219.9).
Notes
The SY1 state variable is a relatively equal weighting of six indicators from the World Development Database plus the KOF Index of Globalization, the Ecological Footprint (EF) and the UN Human Development Index (HDI). The FR2 index is (EF - EnergyUse) and the FR3 index is (Unemployment-Globalization) error correcting controllers (ECC), respectively. The major component creating the collapse in Syria is FR2, the environmental component. It should come as no surprise that Syria is in environmental crisis (here).
The SY20 model has no indicators describing the now-collapsed Syrian dictatorship so the future will be dominated by continuing environmental problems and globalization-driven unemployment. A government of rebel commanders is unlikely to address any of the issues that led to collapse
The SY20 model also does not capture trade relations, particularly with Russia (a vital supplier of essential commodities). I will cover Syrian Trade in a future post.
You can run the SY20 BAU model here. The model is unstable (see the System Matrix below).
Sunday, December 8, 2024
Word-System (2000-2100) Collapse of Syria
Notes
The SY1 state variable is a relatively equal weighting of six indicators from the World Development Database plus the KOF Index of Globalization, the Ecological Footprint (EF) and the UN Human Development Index (HDI). The FR2 index is (EF - EnergyUse) and the FR3 index is (Unemployment-Globalization) error correcting controllers (ECC), respectively. The major component creating the collapse in Syria is FR2, the environmental component. It should come as no surprise that Syria is in environmental crisis (here).
The SY20 model has no indicators describing the now-collapsed Syrian dictatorship so the future will be dominated by continuing environmental problems and globalization-driven unemployment. A government of rebel commanders is unlikely to address any of the issues that led to collapse.
You can run the SY20 BAU model here.
Saturday, December 7, 2024
US Healthcare Expenditures: Three Futures
After 2020, my state space models generate these projections: (1) If Healthcare (HC) expenditures keep pace with government health care expenditures (the black line in the figure above), expenditures will peak at a high level sometime after 2020. (2) If HC expenditures are driven by the World system (WL20) or the US system (USL20), they will continue to decline until well after 2020.
The Trump II Administration, scheduled to take office in early 2025, seems to favor privatizing the entire system which in some way might not be very different from the current system and might well be worse if providers are allowed to charge whatever they want for procedures and medicines.
Notes
My recommendation is to control the US Healthcare system with policy wedges similar to proposals to control CO2 Emissions with policy wedges.
Thursday, December 5, 2024
World-System (1980-2100) Six Futures for France
The New York Times (here) is reporting that the recent collapse of the French government will "...further burden its weak economy" and have ripple effects across Europe. The analysis, however, might be confusing cause and effect. Weakness in the European Union (EU) economies, to include France, might be creating the observed political instability. What I want to explore, starting with France, is whether we are observing the emergence of Steady State Economies in the EU, and that this should not be confused with "weakness". Business commentators and economists, at least in the US, seem convinced that economies can grow forever or, at least, for the foreseeable future. For example, the DICE model (a neoclassical integrated assessment model) grows forever unless a limit is put on technological change. So, it is no surprise that the FR20 (France Twentieth Century model, the dashed blue line marked FR) driven by the US Economy grows forever (dashed red line marked US in the graphic above). Unfortunately, for neoclassical economic theory, this is not the best description of the current French economy using the Akaike Information Criterion (AIC).
Three other models, the Random Walk (RW, dashed blue), the Business As Usual (BAU, black line) and the EU model (right beneath it) are probably what classical economists would identify as the Steady State Economy. Growth reaches an asymptote around 2100. Finally, the FR20 model is driven into collapse mode by the World System (dotted green line).
If you prefer central tendencies in your forecasts, then you probably would conclude that the Steady State Economy is the most likely future. If you are a techno-optimist, you will probably prefer the US-driven future. If you are a Degrowth advocate, you will probably prefer the FR or the W scenario.
Without committing myself to some unknowable future, it seems clear to me that the steady-state and collapse scenarios will not be accepted without resistance. Demonstrators will take to the streets, governments will fall, right-wing political groups will grow in appeal and we will enter a period of chaos. Maybe this is why the Infinite-growth scenario is so appealing.
Notes
FR1 is the dominant state variable of the FR20 system with data taken from the World Development Indicators (WDI). The methodology used to create forecasts is similar to the one used by the Atlanta Federal Reserves GDPNow app. Prediction intervals are generated using a Bootstrap algorithm in the R programming language.
The FR1 state variable was created from the following weighted indicators (the first row of the Measurement Matrix) and explain 98% of the variation.
The first six indicators in standard scores are taken from the World Development Indicators (WDI). KOF = KOF Index of Globalization, EF = Ecological Footprint, HDI = Human Development Index. The second two components: FR2=(CO2+EF-KOF) and FR3 = (LU-L-N-HDI) describe environmental and Unemployment Error Correction Controllers (ECCs).
You can run the FRL20-BAU model here.
Wednesday, December 4, 2024
French Debt, Collapse of the Government and COVID-19, World-System (1950-Present)
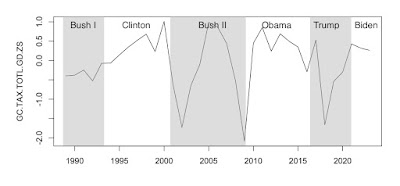
If the currency-inflexibility problem is not resolved, the forecast for (Q-DEBT) in the graphic above is for increasing problems, especially when future shocks create instability.
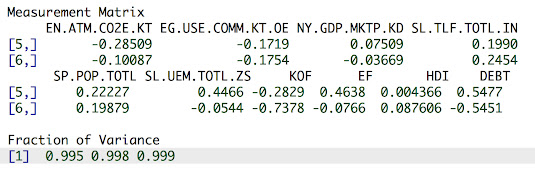
One question you might have is how important DEBT is to the French Economy. If we include DEBT in the Measurement Matrix (below) is doesn't become important until the Fifth and Sixth components and explains under 0.3% of the variation.
The two debt components, FR5 and FR6, capture the (DEBT+Unemployment+Ecological Footprint-KOF Globalization) and (L+KOF-DEBT) controllers, respectively.
Notes
The FR1 state variable was created from the following weighted indicators (the first row of the Measurement Matrix) and explain 98% of the variation.
The first six indicators are taken from the World Development Indicators (WDI). KOF = KOF Index of Globalization, EF = Ecological Footprint, HDI = Human Development Index. The second two components: FR2=(CO2+EF-KOF) and FR3 = (LU-L-N-HDI) describe environmental and Unemployment Error Correction Controllers (ECCs).
You can run the FRL20-BAU model here.
Tuesday, November 26, 2024
US CO2 Forecasts: Will Trump II Make a Difference?
Project 2025
Thursday, November 21, 2024
US Inequality
Causes of Income Inequality
Thursday, November 14, 2024
US Taxes
The assumption is that these cyclical tax cuts help the wealthy and fuel the deficit. I will look at the effects of tax cuts in a future post, but for the present I want to emphasize that tax cuts are both a political football and a countercyclical approach to balancing the economy. Tax cuts could probably be a more effective automatic stabilizer if politics was more rational.
Wednesday, November 13, 2024
Alternate Futures for the US
The graphic above (click to enlarge) shows four alternative futures for US1, an index of overall growth in the US SocioEconomic System (see the measurement matrix below). It is based on computer simulations of alternative estimated state space models. I would argue that the graphic says a lot about why US voters decided the way they did in the 2024 Presidential Election and what we can expect from the new, Right-Wing Republican Administration after 2025.
First, why did the MAGA movement embrace an extension of the American First isolationist movement? The Foreign Policy of the Obama Administration (2009-2017) was directed toward the World System and was not Isolationist. The World System input model (W) in the graphic above put the US on a slower overall growth path (dotted green line). I would argue that voters were well aware that growth of the US Economy and the US standard of living was slowing (see Economist Kathryn Ann Edward's comments here). The realization led to a Right-Wing backlash (the same thing that happened in Germany during the Inter-War (WWI-WWII) Years, see Arno Mayer's The Persistence of the Old Regime).
Second, the President-elect's policy pronouncements and transition plans suggest abandoning the World System and doing everything possible to stimulate unlimited endogenous economic growth in the US: eliminating regulation, ignoring white-collar crime, closing borders to immigrants, abandoning environmental regulation (allowing businesses to exploit free environmental resources), eliminating labor regulation (a restraint on profits), dismantling the Welfare State, slashing business taxes (another restraint on profits), eliminating funding for and control over education (a stimulus to wage growth and a limit on profits), etc.
The red and the blue dashed lines in the graphic above show possible time paths for the US Economy unleashed. The models predict uncontrolled, unending exponential growth for the US System. They are, I would argue, a business man's fantasy. Nothing can grow forever and eventually limits will be reached (my models suggest sometime after 2050). Most of us living at the present moment, me included, will be dead by then. It will be someone else's problem.
There is another possible time path for the US SocioEconomic System: the Random Walk (RW, the solid line in the graphic above). No one can know the future. Attempts to dismantle failing US Institutions may or may not happen as imagined. The new Administration's cabinet picks, so far, are not reassuring. Essentially, in a Random Walk, today is like yesterday except for random error, actions by people who are making it up as they go along.
I am always surprised that commentators can seem so confident about what happened in the 2024 Presidential election and what will happen as a result of it. I'm not. My advice for the future is to take defensive positions and not follow Economic Bubbles that might develop in response to crippling of US regulatory institutions.
We know our current systems are failing and need to be rebuilt. In future posts I will look more carefully at all of these systems.
US Measurement Matrix
The graphic at the beginning of this post applies the weights from row [1,] of the state space measurement matrix to 36 indicators of US development from 1950-2010. After 2010, the results are simulated from four state space models: RW (Random Walk), W (World System input), US (components from rows [2,] and [3,] in the measurement matrix), and BAU (a Business as Usual model with no inputs).
Measurement Matrix
L.US.E. L.US.U. GDP.US. GDP.C. GDP.I. GDP.X.
[1,] 0.1955 0.138 0.1978 0.1972 0.1961 -0.1402
[2,] 0.0669 0.200 -0.0462 -0.0554 -0.0355 0.0751
[3,] -0.0312 0.239 0.0284 0.0314 -0.0272 0.2229
GDP.G. P.US.TBILL. P.CPAPER. P.FED.FUNDS. P.CPI.
[1,] 0.1976 0.00429 -0.01554 0.0127 0.19773
[2,] -0.0377 0.40583 0.40460 0.3998 0.00996
[3,] 0.0541 0.07630 -0.00165 0.0986 0.02128
P.GDP. P.SP500. V.NYSE. P.S.P.DPR. P.S.P.EPR.
[1,] 0.1967 0.1868 0.166 -0.146 -0.112
[2,] 0.0337 -0.1076 -0.131 0.144 0.128
[3,] 0.0240 -0.0277 0.165 0.321 0.384
Q.H.Starts. K.US. M1 M2 P.WPI. Q.A.
[1,] -0.0202 0.1974 0.1953 0.1979 0.1932 0.1918
[2,] 0.0392 -0.0418 -0.0145 -0.0325 0.0612 0.0766
[3,] -0.4666 0.0446 -0.0318 0.0472 0.1051 -0.0973
Q.I. O.B. P.FUELS. P.W.AG. P.W.MFG. Q.OIL.
[1,] 0.1967 -0.173 0.1834 0.1983 0.1990 -0.113
[2,] 0.0374 0.186 0.0269 0.0131 0.0125 0.312
[3,] -0.0683 0.110 0.2538 0.0489 0.0232 -0.145
N.US. IMM.US. U.US. CAPU EF Globalization
[1,] 0.1951 0.1440 0.1967 -0.141 0.1867 0.0818
[2,] 0.0746 0.0546 0.0477 -0.153 0.1096 -0.2964
[3,] -0.0642 -0.1371 -0.0589 -0.164 0.0303 0.3905
CO2 Q.FOSSIL.
[1,] 0.180 0.129
[2,] 0.155 0.283
[3,] -0.110 -0.157
Fraction of Variance
[1] 0.698 0.854 0.900